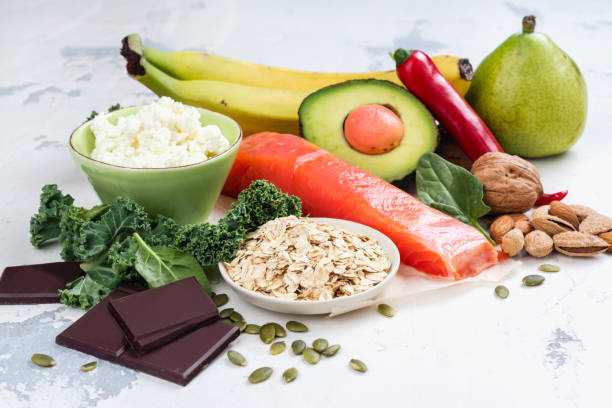

The Dopamine Diet focuses on how specific foods and nutrients can influence dopamine production, impacting mood, motivation, and focus, ultimately aiming to improve eating habits and overall well-being.
Here’s a more detailed look at the concept:
Understanding Dopamine and Its Role:
- Dopamine’s Function:Dopamine is a neurotransmitter (a chemical messenger in the brain) that plays a crucial role in reward, motivation, focus, and pleasure.
- The Reward System:When you experience something pleasurable, your brain releases dopamine, reinforcing that behavior and making you want to repeat it.
- Dopamine and Food:Certain foods, particularly those high in sugar and fat, can trigger a release of dopamine, leading to cravings and potentially unhealthy eating habits.
The Dopamine Diet Approach:
- Nutrient-Rich Foods:The diet emphasizes consuming foods that provide the building blocks for dopamine production, like tyrosine, an amino acid found in protein-rich foods.
- Protein Sources:Lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, and legumes are good sources of tyrosine.
- Antioxidant-Rich Foods:Fruits and vegetables, especially berries and leafy greens, are rich in antioxidants that protect dopamine-producing neurons from damage.
- Whole Foods:The diet encourages eating whole, unprocessed foods, which provide a wider range of nutrients and support overall health.
- Mindful Eating:The Dopamine Diet also emphasizes mindful eating, focusing on being present with your food and paying attention to your body’s hunger and fullness cues.
Benefits of the Dopamine Diet:
- Improved Mood and Motivation:By supporting dopamine production, the diet can help improve mood, motivation, and focus.
- Reduced Cravings:By focusing on nutrient-rich foods, the diet can help reduce cravings for unhealthy foods.
- Better Eating Habits:The diet encourages mindful eating and a balanced approach to food, promoting healthier eating habits overall.
Discover how dopamine, the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, influences your diet, motivation, and cravings. Learn strategies to use this powerful chemical to stay committed to healthy eating and long-term wellness.
Introduction: Understanding the Link Between Dopamine and Dieting
Dopamine, often called the brain’s “feel-good” neurotransmitter, plays a crucial role in our motivation, pleasure, and reward systems. It is also instrumental in regulating our food cravings and dietary choices. In the context of dieting, dopamine’s influence can make or break your commitment to healthy eating. The reason why we may feel an intense urge to indulge in comfort foods or struggle to stay on track with our diet plans lies in the brain’s reward system, primarily mediated by dopamine.
This article explores the science behind dopamine’s role in dieting and offers practical tips on how to use this knowledge to stay motivated on your health journey. By the end, you’ll better understand the ways dopamine can be leveraged to enhance your eating habits, reduce unhealthy cravings, and maintain focus on your long-term health goals.
What Is Dopamine, and Why Does It Matter for Dieting?
The Role of Dopamine in the Brain
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in various essential brain functions, including motivation, reward, pleasure, and learning. It is released when we experience something
pleasurable or rewarding, such as eating foods that taste good or achieving a goal. This release of dopamine reinforces behavior, encouraging us to repeat the action in the future.
Dopamine and the Reward System
The brain’s reward system is designed to encourage behaviors that promote survival and well-being, such as eating, socializing, and mating. When we engage in these behaviors, dopamine is released, creating feelings of pleasure and reinforcing the actions that led to the reward. This is why we often crave foods high in sugar, fat, or salt—because they trigger a massive release of dopamine, making us feel good in the short term.
However, the challenge in dieting arises when the brain’s reward system becomes over-stimulated by highly palatable, calorie-dense foods, causing us to develop cravings and an unhealthy relationship with food. Understanding this connection is essential to creating a healthy eating plan that supports both your body and brain’s needs.
How Dopamine Influences Food Choices and Cravings
The Dopamine Cycle: Cravings and Reward
When you eat a food that you find delicious, dopamine is released, signaling to your brain that this is a behavior worth repeating. The more dopamine released, the more likely you are to crave the same food in the future. This cycle can lead to overconsumption of unhealthy foods—foods that are often high in sugar, fat, and salt—because they trigger larger dopamine spikes compared to healthier, less calorie-dense options.
For instance, processed foods like chocolate, chips, and fast food are designed to activate the brain’s reward system quickly, making them highly addictive. This is why it can be so difficult to resist cravings for junk food, even when you know it’s not aligned with your health goals.
Dopamine and Emotional Eating

In addition to responding to physical hunger, dopamine is also involved in emotional eating. When we’re stressed, anxious, or feeling low, our brains might crave dopamine-boosting foods as a way to self-medicate and alleviate negative emotions. This is why comfort foods like ice cream or pizza become so appealing when we’re feeling down—they offer immediate relief and trigger the release of dopamine, momentarily improving our mood.
While this can feel good in the short term, emotional eating can lead to unhealthy habits and long-term weight gain if not managed effectively. Understanding the emotional triggers behind cravings can help you make healthier choices in moments of stress or emotional turmoil.
The Science Behind Motivation and Willpower in Dieting
How Dopamine Shapes Motivation
Motivation, the drive to pursue goals, is intimately tied to dopamine. In the context of dieting, motivation is necessary for sticking to healthy food choices, resisting temptation, and achieving long-term goals. When you experience success in your diet, whether it’s losing weight or sticking to a meal plan, dopamine is released, reinforcing positive behavior and making you more likely to stay motivated.
On the other hand, a lack of dopamine release can make dieting feel like an uphill battle. If you don’t experience enough reward from your efforts, your motivation may dwindle, leading to diet fatigue and eventually giving in to cravings or abandoning your healthy eating goals altogether.
The Role of Anticipation in Dieting
Interestingly, dopamine is not only released after achieving a reward—it’s also released in anticipation of a reward. This is important when it comes to dieting because the expectation of eating a healthy, satisfying meal can trigger dopamine release, enhancing motivation and making it easier to stick with your plan. In fact, simply planning your meals and anticipating the enjoyment of a delicious, nutritious dish can make the process of dieting feel more rewarding and less restrictive Strategies for Using Dopamine to Stay Motivated in Your Diet
1. Set Clear, Achievable Goals
One way to leverage dopamine in dieting is by setting clear, achievable goals. Research shows that setting small, manageable targets can trigger dopamine release as you work toward them. Whether it’s tracking your calorie intake, exercising regularly, or aiming to try new healthy recipes, breaking down your larger goal into smaller, attainable steps can help maintain your motivation.
As you reach these small milestones, the release of dopamine will reinforce your positive behavior, making it easier to stay on track and build momentum.
2. Reward Yourself with Healthy Dopamine Boosters
Instead of turning to sugary or processed foods to reward yourself, look for healthier alternatives that can still provide a dopamine boost. For instance, activities like exercising, spending time with loved ones, enjoying a hobby, or even taking a warm bath can stimulate dopamine release without derailing your diet. Incorporating these healthy rewards into your routine can help balance your dopamine levels and reduce cravings for unhealthy foods.
3. Eat Foods that Support Dopamine Production
Certain foods can help support your brain’s natural dopamine production, making it easier to stay motivated in your diet. Foods rich in the amino acid tyrosine, such as lean meats, eggs, soy products, and dairy, are particularly beneficial for dopamine synthesis. Additionally, foods high in antioxidants, such as berries, dark chocolate, and leafy greens, can help protect dopamine-producing cells in the brain.
Eating a diet rich in these dopamine-boosting nutrients can enhance mood, reduce cravings, and improve overall motivation, making it easier to stay committed to healthy eating.
4. Practice Mindful Eating
Mindful eating is a powerful tool for enhancing the dopamine experience around food. By slowing down and truly savoring your meals, you can enhance the pleasure and satisfaction you get from healthy foods, leading to greater dopamine release. This practice helps you become more attuned to your hunger and satiety cues, making it easier to avoid overeating and indulging in unhealthy foods.
Research has shown that people who engage in mindful eating report feeling more satisfied with their meals, which can reduce cravings and promote healthier food choices. Additionally, mindfulness can help you identify emotional triggers that lead to overeating, allowing you to address the root cause of your cravings.
The Dopamine-Driven Dieting Pitfalls to Avoid The Downside of Instant Gratification
While dopamine can be a powerful motivator, it’s essential to be aware of the pitfalls of relying too heavily on instant gratification. Highly processed foods can trigger massive dopamine spikes, but these rewards are short-lived. Over time, the brain may require larger doses of these foods to experience the same pleasure, leading to overeating and potentially sabotaging your dieting efforts.
To avoid this trap, it’s essential to focus on long-term rewards, such as improved health, weight loss, and better energy levels. Remind yourself that the temporary pleasure of unhealthy foods is not worth the long-term consequences, and shift your focus toward the lasting benefits of healthy eating.
Dopamine Deficiency and Dieting Fatigue
Chronic dieting without adequate reward or progress can lead to dopamine depletion, making it harder to stay motivated and increasing the likelihood of giving up. This is why it’s so important to celebrate your small wins and build a diet plan that includes rewards, variety, and flexibility. A restrictive or monotonous diet can leave you feeling deprived, reducing dopamine release and making it harder to stay on track.
To combat this, ensure that your diet includes a variety of nutritious foods that satisfy both your physical hunger and your brain’s need for enjoyment. Balance is key to maintaining healthy dopamine levels without falling into the trap of unhealthy food rewards
Building Long-Term Healthy Habits with Dopamine
While short-term motivation driven by dopamine can help you achieve immediate goals, the real challenge in dieting lies in maintaining long-term success. Dieting is not just about achieving a specific weight or physical appearance—it’s about building sustainable, healthy habits that can improve your life over time. Dopamine can help with this, but it requires thoughtful planning and consistency.
Creating a Dopamine-Friendly Environment
One of the most effective ways to support long-term success in dieting is by designing an environment that aligns with your goals and reinforces dopamine-driven behaviors. This might mean:
- Stocking your kitchen with healthy, dopamine-boosting foods: Fill your pantry with fresh fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Having healthy options readily available can help you avoid impulsively reaching for unhealthy, dopamine-triggering foods.
- Limiting temptation: If you’re trying to resist foods that lead to overeating, consider removing them from your home entirely. When temptation is out of sight, it’s easier to avoid the emotional triggers that would otherwise make you reach for unhealthy snacks.
- Incorporating mindful eating rituals: Create an atmosphere that supports mindful eating by setting aside distractions during meals, such as turning off the TV or putting down your phone. This allows you to be present and fully enjoy the sensory experience of your food, triggering a satisfying dopamine response.
- The Role of Physical Activity in Dopamine and Dieting
- Exercise plays a vital role in managing dopamine levels. Physical activity stimulates the release of dopamine, helping to boost mood, reduce stress, and improve overall motivation. In fact, regular exercise has been shown to increase dopamine receptor density in the brain, which can enhance the brain’s sensitivity to the dopamine released during rewarding behaviors.
- If you’re finding it difficult to stay motivated with your diet, consider incorporating more movement into your routine. This doesn’t necessarily mean committing to hours at the gym—simple activities like taking a brisk walk, dancing, or practicing yoga can enhance dopamine release and support your diet plan.
- Additionally, combining exercise with healthy eating can create a positive feedback loop: the more you exercise, the more dopamine your brain releases, making it easier to stick with your eating plan.
- The Importance of Sleep for Dopamine Regulation
- Quality sleep is another essential component for maintaining
healthy dopamine levels. Sleep deprivation has been shown to reduce the number of dopamine receptors in the brain, making it harder to experience the same levels of motivation and reward. Moreover, lack of sleep can increase cravings for high-sugar, high-fat foods, which further exacerbates unhealthy eating patterns.
Prioritize sleep by establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a calm sleep environment, and limiting exposure to screens before bed. When your brain gets the rest it needs, it’s easier to regulate dopamine, stay motivated, and resist unhealthy cravings.
Dealing with Dieting Setbacks: Staying Resilient in the Face of Dopamine Disruptions
Even with all the tools and knowledge available, setbacks are a natural part of any dieting journey. There may be times when you fall off track, indulge in comfort foods, or lose motivation. However, it’s important to remember that dopamine’s influence is not deterministic. You have the power to reframe setbacks and turn them into opportunities for growth.
Reframing Setbacks as Opportunities for Growth
When you indulge in a food you’re trying to avoid, instead of focusing on guilt or disappointment, view the experience as an opportunity to learn. Reflect on why you ate the food—was it due to stress, habit, or emotional reasons? Understanding the root cause behind your choices allows you to identify areas for improvement and helps you re-engage with your healthy eating plan.
Additionally, viewing small setbacks as part of the process rather than as failures will prevent you from feeling demotivated. Research suggests that focusing on progress, rather than perfection, is more likely to lead to sustainable, long-term behavior change. Setbacks provide valuable insights into your triggers, giving you a chance to adjust your strategy and strengthen your commitment to healthy eating.
The Role of Support Systems in Maintaining Motivation
Having a support system is another key factor in staying motivated during dieting. Sharing your goals with friends, family, or an online community can create a sense of accountability and provide positive reinforcement when you succeed. Support systems help you stay focused when dopamine-driven cravings hit and can remind you of your larger purpose when motivation wanes.
Join fitness or nutrition groups, engage in online forums, or consider working with a dietitian or personal trainer. These connections not only provide guidance but also trigger positive dopamine releases from social interactions and support.
Sample Dopamine Menu
Appetizers
- Do a 5-minute stretch
- Listen to your favorite song
- Hug a loved one or pet
Mains
- Go on a 30-minute walk in nature
- Read a chapter of an inspiring book
- Cook a wholesome dinner
Sides
- Enjoy tea while writing your to-do list
- Listen to an educational podcast while commuting
Desserts
- Scroll through social media
- Watch a favorite TV show
Beyond Dieting: How Dopamine Affects Our Relationship with Food
Understanding dopamine’s role in dieting is just one part of the picture—it also influences our broader relationship with food. Many individuals struggle with food because they view it through a lens of guilt or indulgence. Over time, this negative relationship with food can undermine mental and emotional well-being. Here, dopamine’s role can also help shift the way we think about food from being a source of comfort or stress to a source of nourishment and satisfaction.
Redefining Food as Fuel and Enjoyment
Instead of seeing food as a temptation to avoid or a reward to indulge in, it’s essential to reframe food as both nourishment and enjoyment. Dopamine can be released when we enjoy healthy meals, and this is where mindful eating comes in.
When we savor a healthy meal—whether it’s a fresh salad, a piece of grilled salmon, or a bowl of hearty vegetable soup—the brain can release dopamine in response to the pleasure derived from taste, texture, and the satisfaction of nourishing the body.
Over time, these experiences of positive reinforcement can help establish a healthy relationship with food, where it becomes a source of joy and well-being rather than guilt or emotional turmoil.
Breaking Free from Food Guilt
Dopamine can also be helpful in managing food guilt. The brain’s reward system can shift when we adopt a healthier mindset and replace self-criticism with self-compassion. This allows us to enjoy foods we like without feeling bad afterward. When you slip up or give in to cravings, it’s crucial to practice self-compassion instead of guilt. This reduces stress and helps maintain healthy dopamine levels, preventing a cycle of emotional eating.
What is Dopamine and How Does it Impact Your Habits?
Before we can discuss harnessing dopamine to build better habits, it’s important to understand what dopamine is and how it works.
As Cleveland Clinic explains, dopamine — sometimes referred to as the “feel good hormone,” the “motivation molecule,” or your brain’s “reward center” — makes you feel pleasure when you’re doing something that your body biologically recognizes as beneficial. However, this biological recognition is based on thousands of years of evolution. It’s not always 100% reliable in identifying what’s valuable to you today in the modern era.
When you eat foods high in fat or sugar, your brain releases dopamine, a feel-good chemical. Your body interprets these foods as rich energy sources, rewarding you for eating them. Despite their lack of health benefits, the dopamine rush can make it easy to crave these foods.
However, you can use this function to your advantage. By giving yourself rewards and positive incentives for completing tasks you normally wouldn’t want to do, you can “trick” your brain into releasing dopamine when completing those tasks, helping you form positive habits as the brain seeks to repeat that dopamine rush and the actions that caused it.
Understanding How Food Influences Your Mood
Your brain needs specific nutrients to produce essential neurotransmitters – the chemical messengers that regulate your emotions and mental state. These neurotransmitters include:
- Serotonin: Your “feel-good” chemical that regulates mood, sleep, and appetite
- Dopamine: The “reward” neurotransmitter that drives motivation and pleasure
- GABA: A calming neurotransmitter that helps reduce anxiety and stress
Research shows that your diet directly impacts the production and function of these crucial brain chemicals. A 2018 study published in Nutritional Neuroscience found that participants who followed a Mediterranean-style diet rich in whole foods experienced a 33% lower risk of depression compared to those following a typical Western diet.
The nutrients in your food serve as building blocks for neurotransmitter production:
- Protein-rich foods provide amino acids necessary for creating dopamine and serotonin
- Complex carbohydrates help regulate blood sugar levels, impacting mood stability
- B vitamins support the synthesis of mood-regulating chemicals
- Omega-3 fatty acids maintain brain cell structure and function
Conclusion
Dopamine plays a crucial role in the regulation of motivation, cravings, and reward systems, making it an essential factor in maintaining a healthy diet. By understanding how dopamine works, we can better navigate the complex relationship between our brains, food choices, and motivation. The challenges associated with dieting, from managing cravings to maintaining long-term commitment, can often be traced back to the brain’s reward system. However, by applying strategies that align with dopamine’s natural processes, such as setting achievable goals, rewarding yourself with healthier alternatives, and incorporating dopamine-boosting foods into your diet, you can stay on track with your health and wellness journey.
Moreover, balancing dopamine release with mindful eating, exercise, and good sleep practices can help create sustainable habits that not only support a healthier body but also a healthier relationship with food. The key is not to rely on instant gratification or temporary rewards but to focus on long-term well-being and satisfaction.
Understanding dopamine’s influence on emotional eating, cravings, and motivation also allows you to recognize when you’re likely to struggle with food-related decisions. With this awareness, you can be more prepared to navigate these challenges and make healthier choices, even in difficult moments. By embracing the role of dopamine in your diet, you’re empowering yourself to build a resilient mindset that promotes lasting change, creating a lifestyle where healthy eating becomes not just a short-term goal, but a lifelong commitment.
Q&A Section
Q: What is dopamine, and how does it affect our eating habits?
A: Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that plays a key role in pleasure and reward systems in the brain. It influences motivation, and when we eat foods that trigger dopamine release, we feel pleasure, which can drive us to repeat those behaviors, including indulging in unhealthy foods.
Q: How can dopamine affect my motivation to stick to a diet?
A: Dopamine release is tied to feelings of pleasure and reward. When we achieve small goals, such as sticking to a diet for a week, dopamine is released, reinforcing the behavior and boosting motivation to continue. The more rewarding the experience feels, the more likely we are to stay motivated.
Q: Can dopamine lead to emotional eating?
A: Yes, dopamine can influence emotional eating. When we are stressed or feeling down, we may crave dopamine-boosting comfort foods that provide temporary relief from negative emotions, which can lead to overeating and unhealthy food choices.
What role does exercise play in dopamine and dieting?
A: Exercise increases dopamine release, which can improve mood, motivation, and energy levels. Regular physical activity not only supports your overall health but also helps regulate dopamine, making it easier to stick to your healthy eating goals.
Q: How can I make healthier food choices when my dopamine system is driving cravings?
A: You can manage cravings by incorporating dopamine-boosting, healthier foods into your diet, such as those rich in protein, healthy fats, and antioxidants. Mindful eating and focusing on the long-term benefits of healthy eating can also help you resist short-term temptations.
Q: Are there foods that can help balance dopamine levels?
A: Yes, foods rich in tyrosine (like lean meats, eggs, soy products, and dairy) support dopamine production. Foods high in antioxidants, like berries and leafy greens, can also help protect dopamine-producing cells in the brain.
Q: How does sleep affect dopamine and motivation for dieting?
A: Poor sleep can reduce the number of dopamine receptors in the brain, making it harder to experience motivation and pleasure. Lack of sleep also increases cravings for unhealthy, dopamine-triggering foods. Prioritizing good sleep hygiene can help maintain balanced dopamine levels and support your dieting efforts.
Q: What are some effective strategies for staying motivated with a diet?
A: Set clear, achievable goals and reward yourself with non-food-related rewards, like spending time with loved ones or enjoying a hobby. Mindfully eat to increase the satisfaction of your meals and consider incorporating regular physical activity to boost dopamine levels.
Q: How can I avoid the pitfalls of instant gratification in dieting?
A: Focus on long-term goals and remind yourself of the lasting rewards, such as improved health and energy. Instead of indulging in unhealthy foods for instant pleasure, practice mindful eating, and choose healthier rewards that contribute to your overall well-being.
Q: What can I do when I experience setbacks in my diet due to cravings or emotional eating?
A: Practice self-compassion, view setbacks as learning experiences, and reflect on the emotional triggers that led to unhealthy choices. Reframe your perspective and get back on track with your goals, remembering that perfection isn’t necessary for progress.