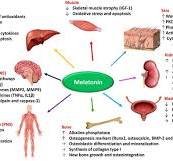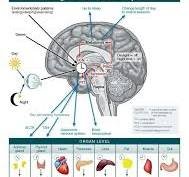
Melatonin is a hormone critical for regulating the body’s sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm) and is closely linked with nutrition, both through dietary intake of its precursors and the timing of meals.
The Role of Melatonin in Sleep
Melatonin is often referred to as the “hormone of darkness” because its production and secretion by the pineal gland is stimulated by darkness and inhibited by light. Its primary function is to signal to the brain and body that it is time to prepare for sleep.
- Circadian Rhythm Regulation: Melatonin helps maintain the body’s internal 24-hour clock by acting on the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus. It reduces the SCN’s wake-promoting signals, which in turn lowers body temperature, blood pressure, and alertness to facilitate sleep onset.
- Sleep Promotion: While not a traditional hypnotic (it doesn’t force sleep in the same way as other sleep aids), melatonin reduces the time it takes to fall asleep (sleep onset latency) and improves overall sleep quality.
- Therapeutic Use: Melatonin supplements are widely used for conditions involving disrupted circadian rhythms, such as jet lag, delayed sleep-wake phase disorder, and sleep issues in children with neurodevelopmental disorders.
The Role of Melatonin in Nutrition
Melatonin’s connection to nutrition is two-fold: the body synthesizes it from a dietary component, and certain foods contain the hormone itself.
- Synthesis from Tryptophan: Melatonin is synthesized from the essential amino acid tryptophan, which must be obtained through the diet. This process also requires B vitamins (B6, B5, B12) as co-factors.
- Dietary Sources: Consuming foods rich in either melatonin or its precursors may increase circulating levels and the body’s antioxidant capacity.
- Nuts (especially pistachios and walnuts) have some of the highest concentrations of melatonin.
- Animal foods like eggs and fish also contain notable amounts.
- Plant-based foods include various cereals (oats, rice, wheat), fruits (cherries, grapes, bananas), and vegetables (tomatoes, peppers, mushrooms).
- Chrono-nutrition: The timing of food intake also plays a role in the sleep-wake cycle. Eating meals at irregular times, especially close to bedtime, can disrupt circadian rhythms and negatively impact sleep quality.
Beyond sleep, melatonin acts as a potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, contributing to functions in the immune system, cardiovascular health, and neuroprotection

Explore how melatonin influences your sleep quality and eating habits, and learn how nutrition can naturally support the production of this essential hormone for better health and well-being.
What Is Melatonin?
Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain. Its primary function is to regulate sleep-wake cycles, also known as circadian rhythms. Melatonin levels naturally rise in the evening as darkness falls, signaling the body to prepare for rest, and decrease in the morning as daylight returns.
Key Functions of Melatonin:
- Regulates Sleep-Wake Cycles: Helps maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
- Supports Immune Function: Plays a role in reducing inflammation and boosting immunity.
- Acts as an Antioxidant: Protects cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals.
How Nutrition Influences Melatonin Production
Foods That Boost Melatonin Production
Certain foods naturally contain melatonin or promote its synthesis in the body. These include:
- Cherries: One of the few natural sources of melatonin, cherries can help improve sleep duration and quality.
- Bananas: High in magnesium and potassium, which relax
- Oats: A rich source of melatonin and complex carbohydrates that help release serotonin, a precursor to melatonin.
- Walnuts and Almonds: Contain melatonin and essential nutrients like magnesium and zinc.
- Fatty Fish: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin D, both of which support melatonin synthesis.
- Nutrients That Aid Melatonin Synthesis
- Tryptophan: An amino acid found in turkey, eggs, and dairy products, tryptophan is converted into serotonin and then melatonin.
- Magnesium: Present in leafy greens, nuts, and seeds, magnesium activates enzymes responsible for melatonin production.
- Vitamin B6: Found in foods like bananas, potatoes, and fortified cereals, B6 aids in the conversion of tryptophan to serotonin.
- Calcium: Present in dairy and fortified plant-based milk, calcium is crucial for melatonin production.
- The Link Between Melatonin and Sleep Quality
- How Melatonin Regulates Sleep
- Melatonin levels rise in response to darkness, making you feel sleepy and signaling your body that it’s time to rest. Low
- melatonin levels, often caused by factors like excessive light exposure or poor diet, can disrupt this process, leading to insomnia or fragmented sleep.
- Melatonin and Sleep Disorders
- Individuals with sleep disorders such as insomnia or jet lag may benefit from melatonin supplementation. However, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
- Impact of Lifestyle Factors on Melatonin
- Light Exposure
- Exposure to artificial light, especially blue light from screens, suppresses melatonin production. Limiting screen time in the evening and using dim, warm lighting can support natural melatonin synthesis.
- Stress
- Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can interfere with melatonin production. Stress management techniques like mindfulness and yoga can help restore balance.
- Diet and Timing of Meals
- Eating large meals or consuming caffeine and alcohol close to bedtime can disrupt melatonin production and impair sleep quality. Aim for lighter, melatonin-friendly snacks in the evening.
- Practical Tips to Enhance Melatonin Naturally
- 1. Optimize Your Diet
- Include melatonin-rich foods like cherries, oats, and walnuts in your diet.
- Eat balanced meals with tryptophan-rich proteins, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats.
- Avoid heavy or sugary foods late in the evening.
- 2. Manage Light Exposure
- Spend time outdoors during the day to boost natural melatonin production.
- Use blackout curtains or sleep masks to ensure a dark sleeping environment.
- Reduce screen time and use blue light-blocking glasses in the evening.
- 3. Establish a Sleep Routine
- Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day to regulate your circadian rhythm.
- Create a calming pre-sleep routine, such as reading or meditating, to signal your body it’s time to wind down.
- 4. Incorporate Relaxation Techniques
- Practice deep breathing or progressive muscle relaxation to lower cortisol levels.
- Engage in activities that reduce stress, such as journaling or listening to calming music.
- 5. Consider Melatonin Supplements if Needed
- Supplements can be helpful for short-term use, such as during jet lag or shift work. Always consult a healthcareprovider before starting supplementation.
- Q1: What is melatonin, and why is it important?
- Ans) Melatonin is a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. It signals the body to prepare for rest and plays a role in immune function and antioxidative protection.
- Q2: Which foods are rich in melatonin?
- Ans) Foods like cherries, bananas, oats, walnuts, and fatty fish are rich in melatonin or support its production.
- Q3: How does light exposure affect melatonin?
- Ans) Exposure to artificial light, particularly blue light, suppresses melatonin production, delaying sleep onset. Reducing evening light exposure can help.
- Q4: Can melatonin supplements help with sleep?
- Ans) Yes, melatonin supplements can improve sleep for conditions like insomnia or jet lag. However, they should be used under medical guidance.
- Q5: How can I naturally boost melatonin production?
- Ans) To boost melatonin naturally, eat a melatonin-friendly diet, manage stress, reduce evening light exposure, and maintain a consistent sleep schedule.