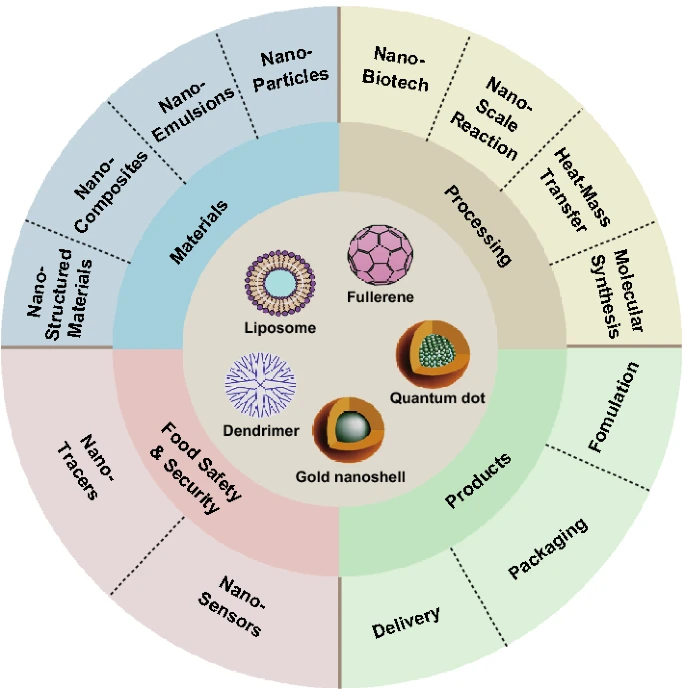
vanced detection techniques.
Here’s a breakdown of how nanotechnology impacts food and nutrition:
1. Enhancing Food Safety and Security:
- Pathogen and Contaminant Detection:Nanotechnology enables the development of nanosensors to rapidly and accurately detect pathogens, toxins, and contaminants in food, ensuring a safer food supply.
- Antimicrobial Packaging:
- Nanomaterials, like silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles, can be incorporated into food packaging to create antimicrobial surfaces, extending shelf life and preventing spoilage.
- Improved Food Processing
- :Nanotechnology can enhance food processing techniques, such as nano-encapsulation, to protect bioactive compounds and improve their bioavailability.
- Smart Packaging:Nanotechnology enables the development of “smart” packaging that can monitor food quality and freshness throughout the supply chain, alerting consumers to potential issues.
2. Improving Nutritional Value and Bioavailability:
- Nano-Encapsulation of Nutrients:
- Nanotechnology allows for the encapsulation of vitamins, minerals, and other bioactive compounds, protecting them from degradation and improving their absorption in the body.
- Enhanced Flavor and Texture:
- Nanomaterials can be used to modify the texture, color, and flavor of food, making it more appealing and palatable.
- Development of Nutraceuticals:Nanotechnology facilitates the development of nutraceuticals, which are food products with added health benefits, by enabling the delivery of specific nutrients or bioactive compounds.
- Addressing Malnutrition:Nanotechnology can play a crucial role in addressing malnutrition by improving the bioavailability of essential nutrients in food.
- 3. Extending Shelf Life and Reducing Food Waste:
- Antimicrobial Properties:Nanomaterials can be used to create antimicrobial surfaces that inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi, extending the shelf life of food products.
- Improved Packaging Materials:Nanotechnology enables the development of advanced packaging materials with enhanced barrier properties, preventing moisture, oxygen, and other factors from damaging food.
- Controlled Release of Preservatives:Nanocarriers can be used to deliver preservatives in a controlled and targeted manner, extending shelf life without compromising food quality.
- 4. Challenges and Considerations:
- Toxicity Concerns:While nanotechnology offers numerous benefits, it’s crucial to thoroughly assess the potential toxicity of nanomaterials used in food applications.
- Regulatory Frameworks:Establishing clear regulatory frameworks for the use of nanotechnology in food is essential to ensure safety and consumer confidence.
- Public Perception:Addressing public concerns and misconceptions about nanotechnology in food is important for its widespread adoption.
Nanotechnology is revolutionizing food production and nutrition by enhancing food quality, safety, and nutrient delivery, while also raising concerns about its long-term health and environmental impact.
Introduction: What Is Nanotechnology and How Does It Relate to Food?
The economic strength of a country mainly depends on agriculture and its products. Improved agricultural practices, including soil preparation and irrigation, are necessary to achieve self-sufficiency in food production and to strengthen a country. Self-sufficiency may be gained by solving agricultural problems, protecting food, and improving farmers’ knowledge about using modern agricultural technologies . Globally, food safety and security are currently receiving a great deal of attention with the aim of ensuring a sustainable supply of nutrient-rich and safe food. Specifically, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is among the largest countries, with approximately 30 million citizens; it has been reported that about 80% of its food demand is met via importing food from other countries, which clearly poses a significant challenge to the economy, food safety, and public health . Moreover, food can also be spoiled by various foodborne pathogens or chemical contaminants, which may cause diseases and sometimes the death of consumers. Thus, to ensure food safety, food handling, distribution, storage, and food quality should be improved; such measures would not only enhance food consumption but also prevent negative effects on consumers’ health
Nanotechnology, the manipulation of matter on an atomic or molecular scale, is a field that has made significant strides in various industries, including electronics, medicine, and food production. In food and nutrition, nanotechnology promises to change the way we produce, process, and consume food. By creating materials and ingredients at the nanoscale (typically in the range of 1 to 100 nanometers), nanotechnology has the potential to improve food quality, safety, and nutritional content. However, its rapid development also raises important questions about its safety and long-term effects.
In this article, we will explore the role of nanotechnology in food and nutrition, its current applications, potential benefits, risks, and the future of this cutting-edge technology.
Nanotechnology is a key advanced technology enabling contribution, development, and sustainable impact on food, medicine, and agriculture sectors. Nanomaterials have potential to lead qualitative and quantitative production of healthier, safer, and high-quality functional foods which are perishable or semi-perishable in nature. Nanotechnologies are superior than conventional food processing technologies with increased shelf life of food products, preventing contamination, and production of enhanced food quality. This comprehensive review on nanotechnologies for functional food development describes the current trends and future perspectives of advanced nanomaterials in food sector considering processing, packaging, security, and storage. Applications of nanotechnologies enhance the food bioavailability, taste, texture, and consistency, achieved through modification of particle size, possible cluster formation, and surface charge of food nanomaterials. In addition, the nanodelivery-mediated nutraceuticals, synergistic action of nanomaterials in food protection, and the application of nanosensors in smart food packaging for monitoring the quality of the stored foods and the common methods employed for
What Is Nanotechnology?
Defining Nanotechnology
At its core, nanotechnology involves working with materials at the nanoscale—the scale of atoms and molecules. The technology has advanced to the point where we can manipulate individual atoms and molecules to create new substances, products, or processes with enhanced properties that would not be possible at a larger scale.
In the context of food and nutrition, nanotechnology refers to the use of nanoscale materials and processes in the production, packaging, and consumption of food. This includes creating food additives that improve texture, flavor, or shelf life, or developing nanocarriers that enhance the bioavailability of nutrients and vitamins.
Why Nanotechnology Matters in Food
Nanotechnology in food production offers several advantages:
- Improved Food Quality: Nanomaterials can be used to enhance the flavor, texture, and appearance of food products, improving the overall consumer experience.
- Enhanced Nutrient Delivery: Nanoparticles can be used to encapsulate vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients, making them easier to absorb and more effective.
- Extended Shelf Life: Nanotechnology can improve food packaging by creating barriers to moisture, air, and light, helping preserve food for longer periods.
- Food Safety: Nanotechnology has the potential to detect contaminants, pathogens, and spoilage in food, improving food safety standards.
The growing interest in nanotechnology has led to a surge in research and development efforts to explore how this technology can improve food systems globally.
The Applications of Nanotechnology in Food and Nutrition Nano-Encapsulation for Enhanced Nutrient Delivery
One of the most promising applications of nanotechnology in food is nano-encapsulation, which involves encapsulating nutrients, flavors, and bioactive compounds inside nanoscale carriers. This process improves the stability and bioavailability of these compounds, making them more effective when consumed.
Improved Bioavailability of Nutrients
Nutrient delivery via nano-encapsulation can significantly enhance the absorption of nutrients like vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. For example, the encapsulation of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) in nanocarriers can improve their solubility and bioavailability, allowing them to be absorbed more efficiently in the body.
Targeted Delivery
Another advantage of nano-encapsulation is that it allows for the targeted delivery of nutrients to specific areas of the digestive system. This means that nutrients can be delivered precisely where they are needed most, ensuring maximum effectiveness.
2. Nano-Packaging to Improve Food Safety and Shelf Life
The food industry constantly faces the challenge of extending the shelf life of products while maintaining their quality. Nanotechnology has made significant strides in food packaging, offering solutions that can preserve food longer and reduce food waste.
Active Packaging
Active packaging refers to packaging that interacts with the food it contains to improve quality and extend shelf life. Nanotechnology can create active packaging materials that release preservatives or antioxidants in response to changes in the food’s environment, such as exposure to light or temperature fluctuations.
Smart Packaging
Smart packaging takes active packaging a step further by incorporating nanosensors that can detect changes in the food’s condition. For example, nanosensors can detect spoilage, contamination, or the presence of harmful bacteria, alerting consumers or manufacturers before the food becomes unsafe to eat.
3. Nano-Sensors for Food Safety
Food safety is a top concern in the global food supply chain. Nanotechnology is helping address this challenge through the development of nano-sensors that can detect harmful pathogens, spoilage, and contaminants in food.
Pathogen Detection
Nanosensors can be designed to detect harmful microorganisms such as E. coli, Salmonella, and Listeria, which are major causes of foodborne illness. These sensors can be embedded into food packaging, allowing for real-time monitoring of food safety.
Contaminant Detection
In addition to detecting pathogens, nanosensors can also identify harmful chemicals, toxins, or pollutants that may be present in food. This technology can be used by food manufacturers to ensure that their products meet safety standards and by consumers to verify the quality of the food they purchase.
4. Nano-Enhanced Food Products
In addition to improving packaging and nutrient delivery, nanotechnology can be used to enhance the properties of food itself. For example, nano-sized particles can be incorporated into food to improve texture, color, and flavor.
Improved Texture and Mouthfeel
Nano-sized ingredients, such as emulsifiers and stabilizers, can improve the texture and mouthfeel of foods like dairy products, sauces, and dressings. These ingredients can create smoother, creamier textures, enhancing the sensory experience of food.
Flavor Enhancement
Nanotechnology can also be used to encapsulate flavors and aromas, allowing them to be released more slowly or targeted at specific times. This technology can be used to improve the flavor profile of food products, enhancing the overall eating experience.
The Potential Benefits of Nanotechnology in Food and Nutrition
1. Increased Efficiency in Food Production
By improving the efficiency of food production and processing, nanotechnology can help reduce waste and make the production of food more sustainable. For instance, the use of nano-based food preservation techniques could reduce the amount of food lost to spoilage, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable food system.
2. Healthier Food Options
Nanotechnology allows for the development of functional foods—foods that provide additional health benefits beyond basic nutrition. These foods can be designed to promote specific health outcomes, such as improved digestion, enhanced immunity, or better heart health, by delivering active ingredients in a more efficient manner.
3. Customized Nutrition
Nanotechnology has the potential to offer personalized nutrition on a much larger scale. With the ability to encapsulate and deliver specific nutrients to target areas of the body, nanotechnology could pave the way for highly personalized nutrition plans tailored to an individual’s specific needs, improving overall health outcomes.
The Risks and Challenges of Nanotechnology in Food
1. Safety Concerns: Are Nano-Materials Safe for Consumption?
As with any emerging technology, nanotechnology raises safety concerns, particularly when it comes to food consumption. The potential for nanoparticles to enter the human body and accumulate in tissues is still not fully understood, and there is concern about the long-term effects of ingesting nanomaterials.
Toxicity of Nanomaterials
The toxicity of nanoparticles is an area of active research. Some studies have suggested that certain nanoparticles could be toxic to human cells, while others have shown no harmful effects. More research is needed to fully assess the potential risks and to establish safety standards for nanomaterials in food.
Bioaccumulation and Toxicity
Nanoparticles have the potential to accumulate in the body over time, and it is unclear whether they could build up in organs or tissues, potentially causing harmful effects. The possibility of bioaccumulation raises questions about the long-term safety of consuming foods containing nanomaterials.
2. Regulatory Challenges
As nanotechnology continues to evolve, regulatory agencies face significant challenges in keeping up with new developments in food production. Current food safety regulations may not be adequate to address the unique risks posed by nanomaterials.
Lack of Standardized Guidelines
At present, there is no global consensus on how to regulate the use of nanotechnology in food. While some countries, like the European Union, have set guidelines for the use of nanomaterials in food, others are still grappling with how to properly assess and regulate their safety.
Need for Research and Standards
In order to ensure the safety of nanotechnology in food, more research is needed to develop standardized guidelines for testing and evaluating the risks associated with nanomaterials. This will help policymakers make informed decisions about how to regulate nanotechnology in food.
The Future of Nanotechnology in Food and Nutrition
1. Continued Innovation in Nutrient Delivery Systems
The future of nanotechnology in food and nutrition will likely see further advancements in nutrient delivery systems, improving the bioavailability and effectiveness of vitamins, minerals, and other health-promoting compounds. Nano-encapsulation techniques could lead to the development of “superfoods” that offer even more concentrated nutritional benefits.
2. Sustainable Food Production
As the global population continues to grow, nanotechnology could play a crucial role in making food production more sustainable. Innovations in nano-packaging, food preservation, and waste reduction could help address the challenges of feeding a growing world population while reducing environmental impact.
3. Personalized and Functional Foods
The future may also bring a shift toward highly personalized nutrition, with nanotechnology enabling the production of custom-tailored food products that meet an individual’s specific dietary needs. Functional foods, designed to promote specific health benefits, could become a standard part of the food landscape, leading to improved public health outcomes.
4. Expanding Food Diversity with Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about food production itself. This can help us diversify and improve the food available to people worldwide, especially in regions facing food insecurity or limited access to certain food products. For example, nanotechnology could enhance the nutritional profile of staple foods, such as rice, wheat, or corn, by fortifying them with essential vitamins and minerals without altering their appearance or taste. This is especially crucial in areas where people rely on a limited number of foods for survival and nutrition.
Further, the precision of nanotechnology allows scientists to experiment with creating entirely new food sources. Synthetic biology and nanotechnology could, in the future, allow for the creation of food products that are nutritionally superior to what nature has provided. Whether it’s creating plant-based proteins that mimic the taste and texture of meat or engineering new sources of essential nutrients in food crops, the potential for expanded food diversity is vast
The Global Implications of Nanotechnology in Food Production
1. The Role of Nanotechnology in Global Food Security
The growing global population and the simultaneous challenge of climate change present significant challenges for the food industry. By 2050, it is estimated that the global population will exceed 9 billion people, placing further strain on the world’s food resources. Nanotechnology could play a pivotal role in addressing these challenges by increasing the efficiency of food production, enhancing food safety, and improving sustainability.
For example, the use of nano-enhanced fertilizers and pesticides could reduce waste and increase crop yields, helping to address food shortages. Nanotechnology can also be used to develop more efficient water usage systems, which could be critical in regions that suffer from droughts and water scarcity. With these innovations, nanotechnology could be a tool for achieving sustainable food production on a global scale, potentially feeding a larger population without increasing environmental degradation.
2. Impact on the Agricultural Industry
The agricultural sector, which is heavily reliant on traditional methods of food production, is beginning to explore the benefits of nanotechnology. From nano-based pest control to advanced soil monitoring systems, nanotechnology could increase crop efficiency and sustainability.
For instance, nano-pesticides could be more effective than conventional pesticides, delivering higher precision and reducing the amount of harmful chemicals that are applied to crops. This could lead to healthier produce with fewer residues and a more sustainable agricultural practice.
Additionally, nano-sensors could be employed to monitor soil quality, moisture levels, and nutrient content. By using sensors that detect these factors at a granular level, farmers could optimize irrigation and fertilization practices, reducing waste and improving crop yields.
3. Nanotechnology’s Environmental Impact
While nanotechnology offers numerous benefits for food production and safety, it is not without its environmental concerns. The production, use, and disposal of nanoparticles in food packaging and processing could lead to unforeseen environmental impacts, especially if these nanoparticles accumulate in ecosystems. For example, nanoparticles used in food packaging could potentially leach into the soil and water supply, affecting local wildlife and plants.
Furthermore, the energy consumption and resources needed to manufacture and apply nanotechnology in food systems must be carefully considered. Over time, the increased use of nanomaterials in food production could contribute to additional environmental strain if not managed sustainably. More research is needed to understand the lifecycle impacts of nanotechnology, including its ecological footprint and the risks of nanoparticles accumulating in the environment.
To address these concerns, policymakers and researchers are advocating for sustainable nanotechnology practices that focus on minimizing environmental risks. The goal is to develop “green nanotechnology” approaches that prioritize environmentally friendly materials and processes while still delivering the benefits of nanotechnology in food systems.
Regulatory Framework for Nanotechnology in Food
1. Current Regulations and Safety Standards
The regulation of nanotechnology in food is a topic of ongoing debate. Different countries have developed varying regulatory frameworks for the use of nanomaterials in food, but many are still working on comprehensive guidelines.
In the European Union (EU), the use of nanotechnology in food is regulated under the Novel Food Regulation, which includes specific guidelines for the safety assessment of nanomaterials in food products. These regulations ensure that any new food ingredients or food additives containing nanomaterials undergo rigorous safety testing before being approved for use in food products.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not yet established a separate regulatory framework for nanotechnology in food, but nanomaterials are generally subject to existing food safety laws. The FDA encourages manufacturers to voluntarily submit safety data for food products containing nanomaterials. However, there remains a lack of standardized testing protocols, making it difficult to assess the risks of nanoparticles in food accurately.
2. Safety Testing for Nanomaterials
One of the primary concerns with nanotechnology in food is the safety of consuming nanoparticles. Since nanoparticles are significantly smaller than traditional ingredients, they can behave differently in the human body, potentially entering cells or tissues more easily. The small size and high surface area of nanoparticles could also make them more reactive, which may pose health risks that are not yet fully understood.
There is a growing need for standardized testing methods to evaluate the safety of nanomaterials in food products. These tests should assess the potential toxicity, bioaccumulation, and long-term effects of nanoparticles on human health and the environment. Currently, researchers are working on developing specific protocols to test for these factors, but the science is still in its infancy.
3. Public Perception and Consumer Confidence
In addition to regulatory challenges, public perception of nanotechnology in food is another barrier to widespread adoption. Many consumers are wary of consuming food that has been engineered or altered using nanotechnology, often due to concerns about the potential risks to health and safety. The lack of comprehensive information about the safety of nanomaterials in food further fuels this uncertainty.
To increase public trust, food manufacturers, regulatory agencies, and researchers must prioritize transparency and clear communication. This includes providing consumers with accurate, science-based information about the safety of nanotechnology in food and offering clear labeling practices for food products containing nanomaterials.
Conclusion: The Future of Nanotechnology in Food and Nutrition
In conclusion, nanotechnology has the potential to revolutionize the food and nutrition industry, offering improvements in food quality, safety, shelf life, and nutrient delivery. Through innovations such as nano-encapsulation, nano-packaging, and nano-sensors, nanotechnology can create smarter, more efficient food systems that can address challenges such as food security, sustainability, and personalized nutrition. With the ability to enhance nutrient bioavailability, improve the safety and freshness of foods, and even offer functional foods tailored to specific health needs, nanotechnology could have a profound impact on public health and the global food industry.
However, alongside its potential benefits, the application of nanotechnology in food comes with significant challenges. Safety concerns regarding the long-term health effects of consuming nanoparticles, the risk of environmental contamination, and the need for comprehensive regulatory frameworks remain key hurdles. For nanotechnology to reach its full potential in food and nutrition, it is crucial to establish standardized safety testing, transparent regulations, and public trust.
The future of nanotechnology in food hinges on striking the right balance between innovation and caution. As research continues to advance, scientists, regulators, and industry stakeholders must work collaboratively to ensure that the benefits of nanotechnology are realized in a responsible and sustainable manner. With careful regulation, education, and ongoing scientific exploration, nanotechnology can contribute to creating a healthier, safer, and more sustainable food system for generations to come.
Q&A Section
Q: What is nanotechnology in food?
A: Nanotechnology in food refers to the use of materials and processes at the nanoscale (1-100 nanometers) to enhance food quality, safety, and nutrition. It includes applications like nano-packaging, nutrient delivery, and food sensors.
Q: How does nanotechnology improve food safety?
A: Nanotechnology enhances food safety by enabling the development of nano-sensors that can detect harmful pathogens, spoilage, or contaminants in food. This allows for real-time monitoring, preventing foodborne illnesses and ensuring product quality.
Q: What is nano-encapsulation, and how does it work in food?
A: Nano-encapsulation involves encapsulating nutrients, vitamins, and bioactive compounds in nanoscale carriers. This improves their stability, bioavailability, and absorption in the body, making nutrients more effective when consumed.
Q: Can nanotechnology extend the shelf life of food?
A: Yes, nanotechnology can create nano-packaging that protects food from moisture, air, and light, which can help extend the shelf life of food by preventing spoilage and degradation.
Q: Are there any health risks associated with nanotechnology in food?
A: While nanotechnology holds great promise, there are concerns about the potential toxicity of nanoparticles when consumed. Research is ongoing to determine their long-term effects on human health, and safety testing is necessary.
Q: How is nanotechnology used in food packaging?
A: Nanotechnology is used to create smart and active packaging that can monitor food conditions, release preservatives, or detect contaminants. These innovations help improve food freshness, reduce waste, and enhance safety.
Q: What are the regulatory challenges of using nanotechnology in food?
A: Current food safety regulations may not be sufficient to address the unique risks posed by nanomaterials. More research is needed to establish standardized testing and safety protocols to ensure the safe use of nanotechnology in food.
Q: Can nanotechnology improve personalized nutrition?
A: Yes, nanotechnology can enhance personalized nutrition by enabling the targeted delivery of nutrients based on an individual’s specific health needs. Nano-encapsulation allows for more efficient absorption of nutrients tailored to personal requirements.
Q: What are functional foods, and how can nanotechnology enhance them?
A: Functional foods are foods that provide health benefits beyond basic nutrition. Nanotechnology can enhance these foods by improving nutrient delivery, increasing bioavailability, and incorporating bioactive compounds that support health, such as antioxidants and probiotics.
Q: How can nanotechnology contribute to food security?
A: Nanotechnology can improve food security by increasing crop yields through the use of nano-fertilizers and pesticides, enhancing food preservation, and reducing waste through smarter packaging and shelf life extension technologies.
